12/05/2017
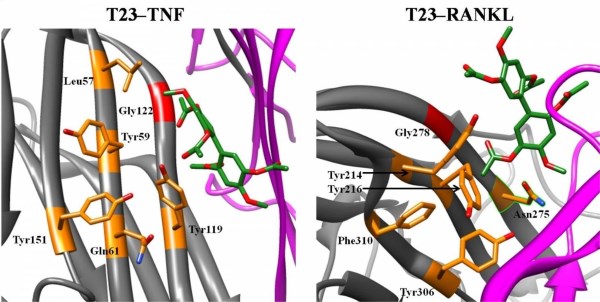
Using a new drug screening approach that combines structure-based with ligand-based in silico modeling, Fleming Researches have identified and confirmed the therapeutic potential of two small molecules targeting TNF (Tumor Necrosis Factor), a key player implicated in the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn's disease, psoriasis and other diseases. These compounds, namely T8 and T23, also inhibit RANKL, a second protein involved in inflammatory processes, that shares molecular characteristics with TNF. T8 and T23 constitute the second and third published examples of dual small-molecule direct function inhibitors of TNF and RANKL. The molecules can be further optimized to develop improved treatments for a range of inflammatory, autoimmune, and bone loss diseases.
The study, titled “Cheminformatics-aided discovery of small-molecule Protein-Protein Interaction (PPI) dual inhibitors of Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) and Receptor Activator of NF-κB Ligand (RANKL)” has been published in PLoS Computational Biology. The study has been highlighted in EurekaAlert, Rheumatoid Arthritis News, Multiple Sclerosis News Today and IBD News Today.