Multiplex ELISA querying the phosphorylation of 27 phosphoproteins/signaling hubs and the secretion of 32 mediators (cytokines, chemokines and growth factors) revealed that Lysophosphatidic Acid (LPA) is a proinflammatory stimulus of renal tubular epithelial cells. Moreover, LPA responses were compared with other 175 biological stimuli, indicating that LPA clusters with other pro-inflammatory growth factors (e.g. TNF, IL1a). [PubMed]
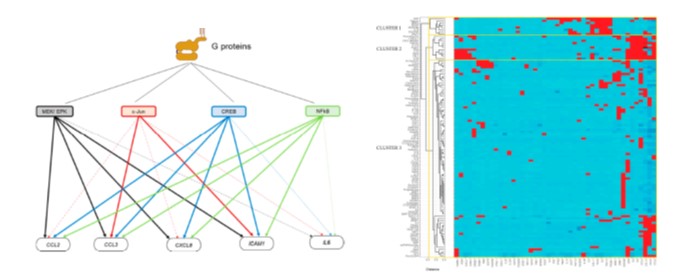
Lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) is a lysophospholipid present in most biological fluids and implicated in a series of diseases. Renal tubular epithelial cells (TECs) are the cells lining the nephrons of the kidneys and are considered to be the initiators of renal tubulointerstitial diseases. In an effort to expand our knowledge on TECs’ signaling and secretion of proinflammatory/profibrotic factors, we exposed the kidney proximal tubular epithelial cell line HKC-8, which derives from normal kidney cortex, to LPA and 175 other inflammatory-immunological stimuli (toll-like receptor (TLR) ligands, cytokines, chemokines, growth factors and drugs). Subsequently, we measured the levels of 27 intracellular signaling hubs (phosphoproteins) as well as of 32 extracellular secreted mediators upon each one of the stimuli employing custom multiplex ELISA. According to our findings, LPA induced the phosphorylation of several signaling hubs such as CREB1, ERK1, IκΒα, JUN, and MEK1 and the secretion of proinflammatory molecules CCL2, CCL3, CXCL10, ICAM1, IL-6, and IL-8. Interestingly, LPA clustered with other pro-inflammatory factors such as cytokines and TLR ligands further proving its proinflammatory role. Moreover, our in vitro experiments with signaling pathway inhibitors suggested that the JNK/c-JUN, MEK/ERK, NFκB, and CREB pathways are implicated in the induction of some of the LPA-mediated secreted factors.